Vitamin D is More Important than You Think
April 5, 2020
Vitamin D is More Important than You Think
By now, everyone knows that getting enough vitamin D is good for your health. Of course, it makes strong bones and teeth. That’s why generations of children were told to drink milk every day. Older people, particularly post-menopausal women, are often given supplements because of their increased risk of osteoporosis. Still, the huge group between young and old hasn’t worried much about getting enough of this vitamin.
In recent years, the medical community has noticed an increase in vitamin D deficient patients. Some experts have called it an epidemic, though not everyone agrees with that characterization. The lack of vitamin D has some serious consequences and can leave you vulnerable to a number of medical conditions. That’s why you should consider taking supplements if you aren’t getting enough of this important vitamin.
What Vitamin D Does
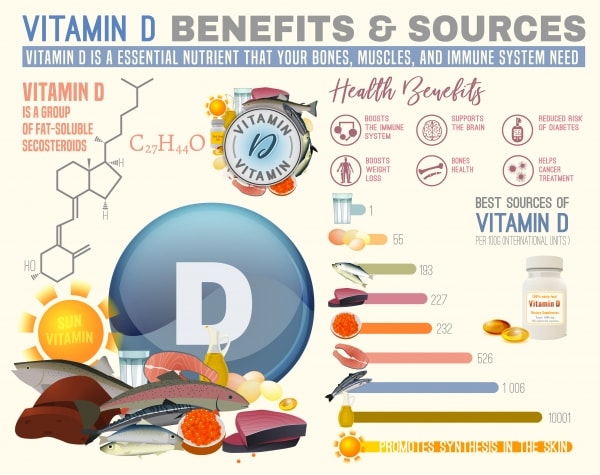
Vitamin D allows your body to absorb calcium so that your bones grow as they should. Children who lack this vitamin may have soft bones, a condition known as rickets. Adults with a deficiency can develop bones that are misshapen and easily broken.
Vitamin D helps you maintain your health in many other ways as well. When you receive proper levels of it, you are less likely to develop breast cancer, colon cancer, and prostrate cancer. Vitamin D also wards off depression, lessens weight gain and may be helpful in combating diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, and autoimmune disease. Some scientists believe that vitamin D may also prevent or treat autism. Vitamin D supplements have been largely embraced by the mainstream medical community, although physicians believe more research needs to be done. However, experts do agree that getting enough vitamin D is essential to maintaining your health.
How Much Vitamin D Do You Need?
Experts do disagree about exactly how much vitamin D you need each day. Currently, the US National Academy of Medicine recommends 600 to 800 IU (international units) each day. Some other experts recommend double that amount or more. Taking too much vitamin D can make you ill, although up to 4000 IU is considered safe for most people. For those with certain medical conditions or a deficiency, higher levels may be in order.
How to Get Enough Vitamin D
Sunshine is the most natural way of getting enough vitamin D. The UV-B radiation from the sun mixes with a type of cholesterol on your skin and produces the vitamin. Around 8 -15 minutes of sunshine each day is considered enough exposure for light-skinned people to get the vitamin D they need, but darker skinned individuals will need more time due to the protective melanin in their skin. Remember, you need unprotected exposure to the sun to produce vitamin D, so wait to apply sunscreen until after the prescribed period.
You can also get vitamin D from certain foods such as fish and seafood. Salmon, tuna, oysters, etc. provide a significant amount of your daily need. Mushrooms and egg yolks are also good sources of vitamin D as are fortified foods like cereals and milk.
How to Use Supplements
The medical community now recommends that all children and teens receive a vitamin D supplement each day due to the large number of young people who are deficient in this vitamin. Children with chronic disease, in particular, need supplements. The American Association of Pediatrics recommends a 400 IU supplement from birth through the teen years. Individual physicians may recommend a higher dose for your child depending on their health, diet and geographical region.
Adults who don’t get enough sun or eat a vitamin D deficient diet should also take a supplement. Taking too much can be harmful, but any amount under 4000 IU should be safe. However, as with all medication and supplements, you should consult your doctor about the proper dosage for you. It is possible that you get enough vitamin D through sun exposure and diet alone, but many people do not, at least not on a regular basis. You may well have a deficiency and not know it.
The medical community now recognizes that vitamin D has a more important role in protecting your health than was previously thought. Of course, it is vital to develop and maintain strong bones and teeth, but it also offers protection from several different cancers, particularly breast, colon and prostate cancer. Low levels of vitamin D are linked to depression, heart disease, high blood pressure and other common ailments and diseases. Although the mainstream medical community is sometimes suspicious of supplements, that is not the case with vitamin D. Experts now largely agree that supplements are essential for children’s health and necessary in the case of many adults.
Search The Blog
Archives
- November 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- February 2024
- October 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- November 2021
- July 2021
- May 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- January 2020